Homocysteine is an amino acid. Vitamins B12, B6 and folate break down homocysteine to create other chemicals your body needs. High homocysteine levels may mean you have a vitamin deficiency. Without treatment, elevated homocysteine increases your risks for blood clots, heart disease and stroke.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
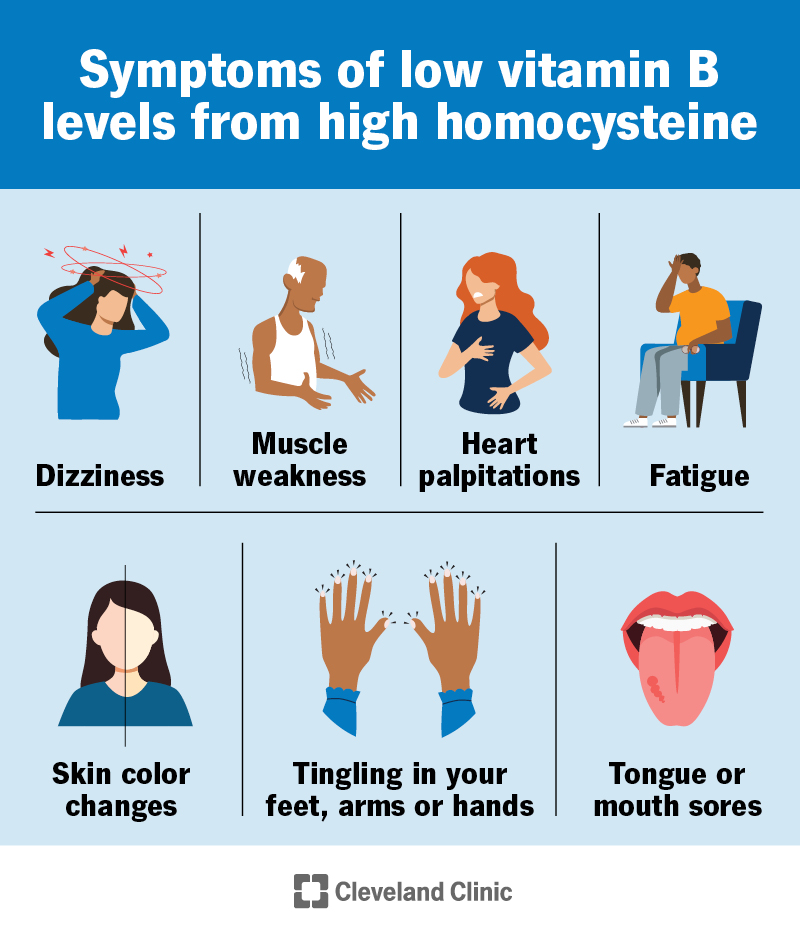
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/homocysteine-refresh-cv)
Homocysteine (Hcy) is an amino acid. It’s a chemical in your blood that helps create proteins. Vitamin B12, vitamin B6 and vitamin B9 (folate) break down homocysteine to generate other chemicals your body needs.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A high level of homocysteine is harmful to the lining in your artery walls. It also may cause blockages in your blood vessels that lead to problems like a heart attack or stroke.
Without a healthy amount of homocysteine, you may feel some adverse effects. A homocysteine test can tell you how much of this amino acid you have in your blood. It should be five to 15 micromoles per liter (mcmol/L).
When it interacts with the B vitamins, homocysteine converts to two substances:
High homocysteine levels could mean you have a medical condition. But other factors can affect your homocysteine (Hcy) blood levels, including:
If you have more than 50 mcmol/L, the excess homocysteine (Hcy) may damage the lining of your arteries (blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood throughout your body).
Homocysteine can make it easier for atherosclerosis (fat and cholesterol buildup) to start. It can also make it worse. High homocysteine levels can also lead to blood clots or blood vessel blockages. Artery damage, atherosclerosis and blood clots raise your risk of:
Advertisement
In a healthy person, homocysteine levels are around five to 15 mcmol/L. Nearly all that homocysteine converts to other proteins. Some people have mild (15 to 30 mcmol/L) or moderate (30 to 100 mcmol/L) levels of homocysteine. More than 100 mcmol/L is a severe level.
Typically, homocysteine (Hcy) breaks down into other substances, and only small amounts of homocysteine remain in your blood. Some conditions interfere with this process and leave you with high homocysteine levels.
You may have too much homocysteine in your blood if you have:
You may need a homocysteine blood test if you have symptoms of a vitamin B deficiency. Common symptoms of vitamin B deficiencies include:
If you have high homocysteine levels, your healthcare provider may recommend taking supplements of:
You may also get more of these nutrients by eating foods that contain them. But increasing your vitamin intake alone doesn’t reduce your risk of heart disease. You can lower your risk of heart disease by:
Homocysteine is an amino acid your body uses. Usually, very little homocysteine stays in your blood. You may be concerned if you have high homocysteine levels, but you can change that. Based on the results of your homocysteine test, your healthcare provider may recommend supplements. They may also suggest that you make changes to your daily habits for better heart and blood vessel health.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
